Understanding the nuances of Qt licensing is pivotal for developers. This comprehensive guide aims to shed light on the intricacies of licensing implications for Qt applications, spanning desktop, embedded, and mobile domains. It also addresses scenarios in both B2B and B2C contexts, offering clarity on GPL, LGPL, and commercial licensing.
To make it more simple, the table below provides a concise overview of the obligations associated with each Qt licensing option. It is categorized by scenarios, including embedded, desktop, mobile, as well as B2B and B2C cases.
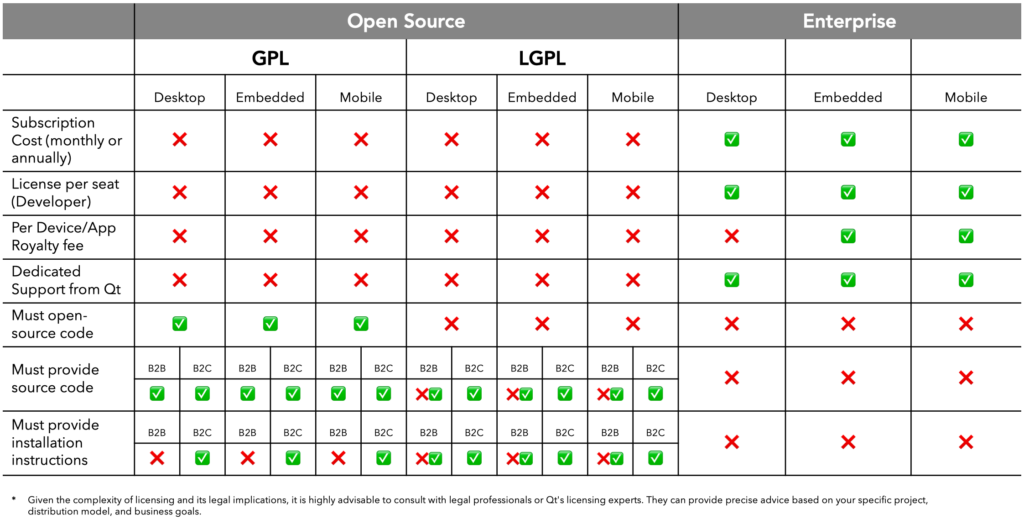
In the table, ‘x’ indicates no obligation, while a checkmark signifies compliance is required.
GPL vs LGPL
When dealing with GPL and LGPL, complexities arise, particularly in B2B and B2C contexts, regarding whether or not to provide the source code to end users, along with installation instructions.
1. GPL Distribution (B2B and B2C):
- Installation Instructions: GPL doesn’t explicitly mandate installation instructions. However, for B2C, it places emphasis on providing access to the complete corresponding source code.
- Access to Source Code: Users must have access to the complete corresponding source code under the terms of the GPL.
2. LGPL Distribution (B2B and B2C):
- Installation Instructions: Similar to GPL, LGPL doesn’t require installation instructions. It focuses on ensuring access to the complete corresponding source code.
- Access to Source Code: LGPL provides more flexibility for dynamically linked libraries in closed-source applications.
Qt Enterprise
Some Qt modules are exclusively available under both commercial and open-source GPL only licenses. These include:
- Qt Charts: A module for creating interactive and feature-rich charts.
- Qt Data Visualization: Used for 3D data visualization.
- Qt Virtual Keyboard: Provides an on-screen keyboard component.
- Qt Wayland Compositor: Provides a framework to develop a Wayland compositor.
However, it’s important to note that the availability of specific Qt modules under different licenses, including commercial and GPL, can change over time. You can refer to this useful link where you can filter all Qt modules and add-ons by license among other options.
Qt Commercial License Costs and Benefits:
- Subscription Model: Commercial licenses may involve a subscription model with costs based on the number of seats (developers).
- Royalty Fees: Enterprise licenses may include per-device or per-app royalty fees for embedded and mobile applications.
- Commercial Support: Qt’s commercial license often comes with dedicated support and additional features.
- Flexibility: Commercial licenses offer more flexibility for closed-source applications, making them suitable for proprietary projects.
You can find out more about costs and benefits here.
Other Licensing Options
Qt for Small Businesses
Designed with the needs of small businesses in mind, the Qt for Small Businesses license offers an affordable solution for harnessing the power of Qt technology. This license is tailored to provide small enterprises with access to the comprehensive features of Qt, enabling them to build robust and visually appealing applications without breaking the bank. Whether you’re developing software for internal use or creating products for your customers, the Qt for Small Businesses license strikes a balance between cost-effectiveness and the rich capabilities that Qt has to offer. Read more about how to obtain it here.
Qt Educational License
The Qt Educational License is a fantastic opportunity for academic institutions, providing students and educators access to the powerful Qt framework for free. This license supports hands-on learning and experimentation with Qt tools and technologies, fostering innovation and skill development. It’s a commitment to empowering the next generation of developers by offering a robust platform for educational purposes, encouraging exploration and understanding of modern software development practices. Read more about how to obtain it here.
Conclusion
Selecting the right licensing model for your application hinges on various factors—consider the required modules, the need for open or closed source code, and whether GPL aligns with your goals. Costs are inevitable, whether in the form of a Qt commercial license or legal consultation to tailor the best solution for your needs. Seeking legal advice is crucial for compliance with licensing terms and addressing unique aspects of your distribution model. Consistent practices across distributions prevent confusion.
Regardless of the chosen license, clear documentation enhances transparency and user comprehension. For those embracing open source, compliance with its spirit and good faith practices is essential, fostering a community built on transparency, compliance, and collaboration. Whether it’s GPL, LGPL, or Qt’s commercial license, a nuanced understanding ensures a positive relationship with the open-source community and a successful application deployment.



Comments (2)
sunil pandya - June 11, 2024
If i am developing my Application for Accounting, then can i use LGPL Qt Licence? Mostly I will not modify the QT Code, I will use it with Python, the Accounting Application I will create, I will sell to end user for their Accounting Preparation need.
Which Licence I should use? Can I use LGPL?
SanthoshKumar - October 2, 2024
You can use LGPL license for your software and its allowed to sell it.
But when you modify the Qt source and redistribute, its must to get the commercial license.